 Everything we do in an organization can be considered as a process, and, whether we realize it or not, every process is affected by variation. We need to understand and manage this phenomenon of variation if we want to achieve the best results.
Everything we do in an organization can be considered as a process, and, whether we realize it or not, every process is affected by variation. We need to understand and manage this phenomenon of variation if we want to achieve the best results.
Let’s look at the process of sales
In our last post ‘Managing Variation: Why Entropy Matters’ we looked at variation and entropy with regard to organizations. In this post we are going to look at variation regarding a process. Let’s consider the sales process of a company. ‘Scoring’ a sale is just the last step of a process that starts with purchasing the raw material, goes through manufacturing and assembly, up to shipment. To be sure we score the sale we have to consider the variation associated with every part of the process:
- the arrival time of raw material
- time to inspect it
- time for moving material from the raw material warehouse to manufacturing
- time for manufacturing
- time for assembly
- time for moving material to the warehouse of finished products
- shipment time
There is no way to ‘predict’ the final outcome of the process without considering the different steps that brought us to the finalization of the sale; the only way is to approach the process ‘holistically’.
Understanding and improving the performances of highly interdependent processes in complex organizations is possible only if we understand:
- the variation associated with single processes,
- the cause-effect relationships among them, and
- the impact that they have individually and cumulatively on the final result
In other words, we have to approach the organization (system) as a whole.
The system as a network
As we know, a system is a network of interdependent components that work together to achieve a common goal. If there is no goal, there is no system. If we have a set of segregated parts, neither interacting, nor interdependent, A, B, C, the Theory of Systems shows that the performance of this kind of network is ‘additive’:
Perf.(system)=Perf.(A)+Perf.(B)+Perf.(C)+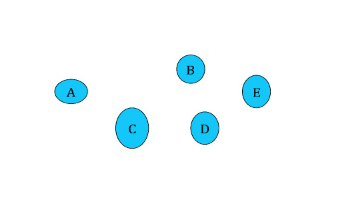 Independent network
Independent network
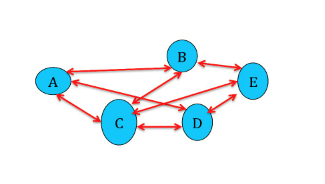
On the other hand, if the components are dependent and/or interacting, the cause-effect relations among the various parts of the system are “non-linear”, and the Theory of Systems shows that:
Perf.(system)=)¹Perf.(A)+Perf.(B)+Perf.(C)+…
Interdependent network
Organizations and complexity
Interdependence and co-variance are elements that influence the “dynamics” of a system.
When we have large interconnected systems, it is virtually impossible to predict the effect that changing a single component will have on the system overall. We face a problem of complexity, where non-linear interactions play an important role.
This post is an extract from the book ‘Sechel: Logic, Language and Tools to Manage Any Organization as a Network’
See also our series on Systemic Management:
Why a Software Can Never Manage a Company
Transforming Industry with a Systemic Approach
Managing Projects the Systemic Way: Critical Chain
The Crucial Role of Synchronization in a Systems-Based Approach to Management
Operating a Systemic Organization: The Playbook
Managing a Systemic Organization: The Information System
The Physics of Management: Network Theory and Us
No Fear in the Workplace – Making It Happen
Drive Out Fear by Learning to Think Systemically
Don’t Climb, Grow! Success in the Systemic Organization
Can We Do Away with Hierarchy?
The Network of Projects: Driving Out Fear in the Post-Digital Age
Fear-free Career Paths in the Network of Projects
Learning, Joy, and the Interconnected Future
Structuring the Network of Projects: Algorithms and Emotions
Start Making Sense: Introduction To Statistical Process Control





I question the Interdependent Network equation – is it really additive? It seems to me that because the network is inter-dependent, then Perf(A) impacts Perf(B), and should therefore be multiplicative, at least to some extent.
While I agree that one needs to view systems holistically, some are amenable to modeling in order to make predictions, at least in relevant ranges. I just posted a piece about this using Queuing Models on my Treasury Cafe blog if you are interested.
Great series and links – thanks!
The difference between the equations for Additive systems and Interactive systems isn’t clear. Perhaps the footnote 1 explains it, but I can’t find it either. Can you fill me in?